Finace
State and Local Government Finances
Understanding how state and local governments spend their money is crucial for informed citizens and policymakers alike. This article delves into the intricacies of state and local government finances, exploring key expenditure categories, trends over time, and the factors influencing spending variations across states.
A Glimpse into State and Local Government Spending
State and local governments play a vital role in providing essential services to their communities. In fiscal year 2021, these entities collectively spent a staggering $3.7 trillion on direct general government expenditures. This vast sum encompasses a wide range of services, with education and healthcare topping the list.

The Breakdown of Expenditures
State and local governments allocate their resources across various categories, with some areas receiving significantly more attention than others. The major spending categories include:
Education
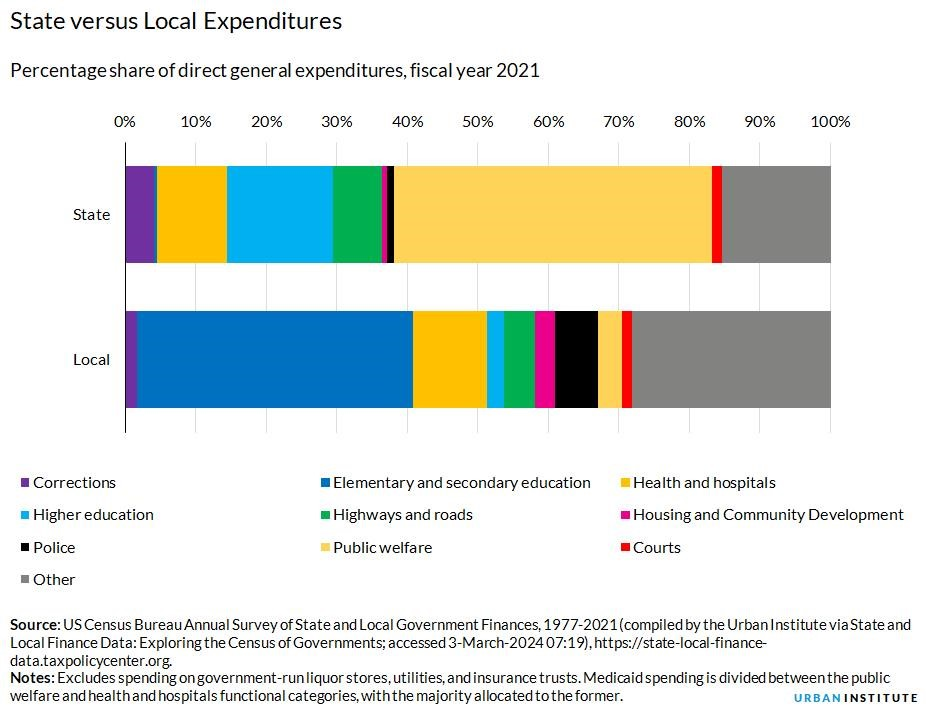
- Elementary and Secondary Education: This category accounts for a substantial portion of state and local spending, often exceeding 30% of their budgets. Local governments are the primary direct spenders in this area, although a significant portion of the funding originates from state and federal sources.
- Higher Education: State governments play a more prominent role in higher education funding compared to local governments. This category typically accounts for around 8% of state and local expenditures.
Healthcare
- Public Welfare: This broad category encompasses a variety of programs, including Medicaid, which is a significant driver of state spending. Medicaid, a joint state and federal program, is responsible for a large and growing portion of state budgets.
- Health and Hospitals: This category accounts for a substantial portion of state and local expenditures, with spending roughly equal at both levels of government.
Infrastructure
- Highways and Roads: Infrastructure investment is another significant area of spending, with state governments investing more directly than local governments.
Public Safety
- Criminal Justice: This category encompasses spending on police, corrections, and courts. Local governments typically allocate a larger share of their budgets to police services compared to state governments.
Other Spending Categories
In addition to these core areas, state and local governments also invest in a variety of other programs, including:
- Housing and Community Development: This category accounts for a smaller portion of overall spending but is essential for supporting affordable housing and community development initiatives.
- Financial Administration and Central Staff Services: This area includes administrative costs, which are typically a smaller but essential portion of state and local budgets.
- Interest on Debt: State and local governments must allocate funds to cover interest payments on their outstanding debt.
- Sanitation: This category includes spending on waste management, water and sewer services, and other sanitation programs.
- Fire Protection: State and local governments allocate funds for fire departments and related services to ensure public safety.
The Divergence of State and Local Spending
State and local governments differ in their spending priorities and the types of services they provide. While both levels of government contribute to public education, local governments are the primary direct spenders, while state governments play a more prominent role in higher education. State governments are also the main direct spenders on public welfare, largely due to Medicaid spending, while local governments dedicate more resources to police services.
State and Local Expenditures: A Historical Perspective
Over the past several decades, state and local government spending has experienced significant growth. From 1977 to 2021, real per capita expenditures doubled, reflecting the growing demand for public services and the increasing complexity of government responsibilities.

Public welfare spending, driven largely by Medicaid, has witnessed the most significant growth, increasing by nearly 500% during this period. Meanwhile, healthcare spending, including hospitals, has also experienced substantial growth, reflecting the rising costs of medical care and the expanding demand for healthcare services.
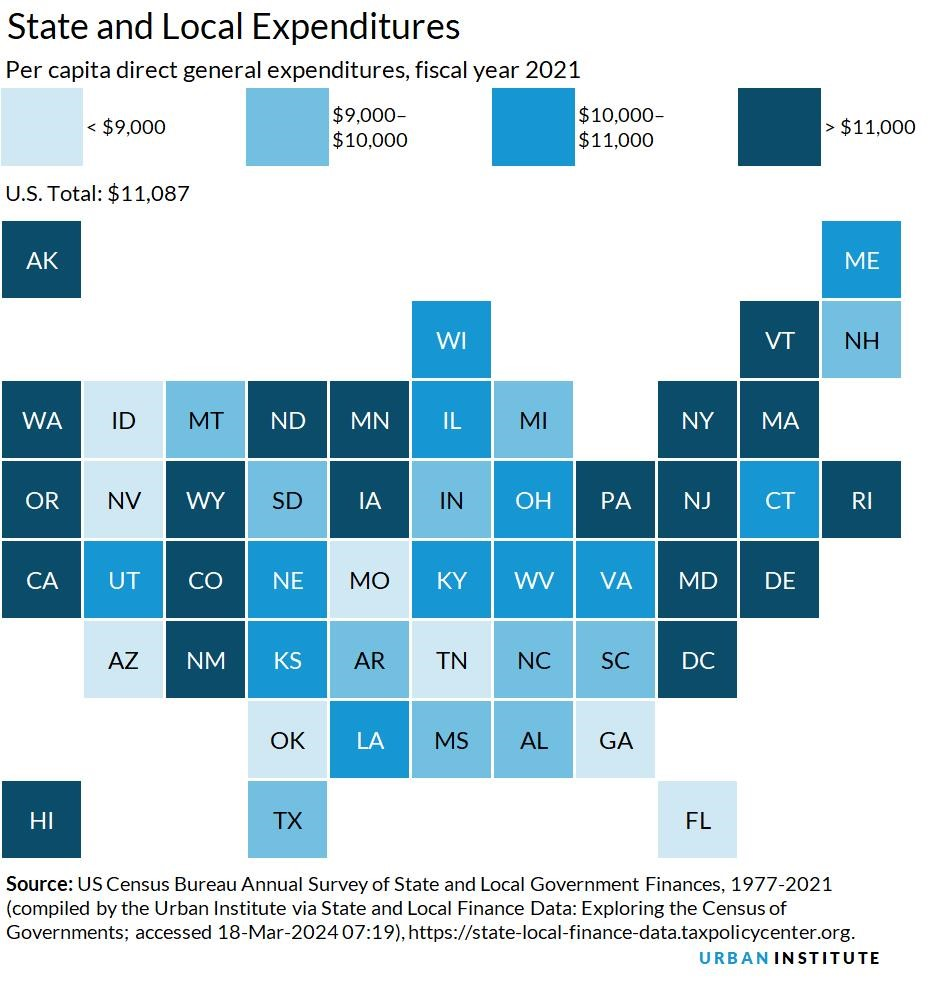
Why Spending Varies Across States
Per capita state and local spending varies considerably across states, reflecting a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Demographics: States with a higher proportion of school-age children, for instance, typically have higher per capita education spending.
- Geography: States with vast rural areas or challenging terrain may face higher infrastructure costs.
- Economic Conditions: States with strong economic growth may generate more revenue and allocate more resources to public services.
- Policy Choices: State governments have significant latitude in setting tax rates, benefit levels, and service delivery models, which can influence spending levels.
Key Takeaways
Understanding state and local government finances is essential for citizens and policymakers. This article has highlighted:
- The significant role state and local governments play in providing public services.
- The key spending categories, including education, healthcare, infrastructure, and public safety.
- The differences in spending priorities between state and local governments.
- The historical trends in state and local government spending.
- The factors influencing spending variations across states.
Learn more about us at: javanet247
By gaining a deeper understanding of these issues, citizens can engage in informed discussions about public policy and hold their elected officials accountable for effective and efficient resource allocation.