Crypto
Layer 3 Crypto: Understanding the Evolution of Blockchain Scaling
The rapid growth of blockchain technology has led to a surge in users and diverse applications, putting strain on layer 1 blockchain networks’ scalability. To address this challenge, layer 2 solutions have emerged, offering faster transactions by moving them to off-chain networks. However, layer 2 solutions lack interoperability, a crucial aspect addressed by layer 3 solutions. This article explores the key differences between layer 2 and layer 3 blockchain networks and their implications for the web3 ecosystem.
Understanding Layer 1 Blockchains
Before diving into the distinctions between layer 2 and layer 3, it’s essential to understand layer 1 blockchains. These form the foundation of the web3 ecosystem, providing the core infrastructure for building decentralized applications (dApps). Examples include Bitcoin, Ethereum, BSC Chain, and Cardano.
Layer 1 networks provide the core infrastructure, including transaction settlement and validation mechanisms for smart contracts, dApps, and other blockchain layers. Importantly, they operate independently, not relying on any other network. Layer 1 networks also bear the responsibility for security and consensus mechanisms for dApps and layer 2 solutions built upon them.

The Inefficiencies of Layer 1
The question of "what is the best layer blockchain?" hinges on the inherent limitations of layer 1 networks. Legacy blockchain networks struggle to keep up with the increasing demands of the web3 landscape, facing significant scalability challenges. For blockchain to become a viable alternative for everyday payments, it needs to process transactions faster than traditional payment service providers. Unfortunately, most legacy blockchains currently lag behind in this regard.
The scalability of blockchain technology is crucial for accommodating a higher volume of transactions. The "blockchain trilemma" highlights the inherent trade-offs between decentralization, security, and performance. Increasing transaction throughput often comes at the expense of decentralization and security.
Another factor contributing to layer 1 scaling issues is the resource-intensive nature of Proof of Work (PoW) mining. While PoW is widely considered one of the most secure consensus mechanisms, it demands considerable computational resources. Scaling layer 1 blockchains using PoW can prove challenging due to the need for additional computing power.
Layer 1 Scaling Solutions
Increasing transaction throughput in layer 1 networks often leads to network congestion, causing slower transaction speeds and higher fees. However, various scaling solutions have emerged to address these issues:
- Block Size Expansion: Enlarging the block size allows more transactions to be processed in each block.
- Consensus Mechanism Modifications: Altering the consensus mechanism can enhance the efficiency of blockchain networks.
- Sharding: This technique involves partitioning blockchain data into different groups (shards), enabling parallel processing and reducing the workload on individual nodes.
- Forking: In cases of disagreement on scalability, the community may create forks in the layer 1 blockchain’s codebase.
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions: Building on the Foundation
Recognizing the challenges of scaling layer 1 networks, layer 2 scaling solutions have emerged. They aim to improve scalability by offloading transactions from the main blockchain, reducing congestion and enhancing throughput. Many layer 2 solutions also inherit the security mechanisms of layer 1 networks, offering a balance between scalability and security.
Layer 2 networks are instrumental in the evolution of blockchain and web3. They support scaling efforts for popular public blockchain networks, such as Ethereum.

Notable Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
-
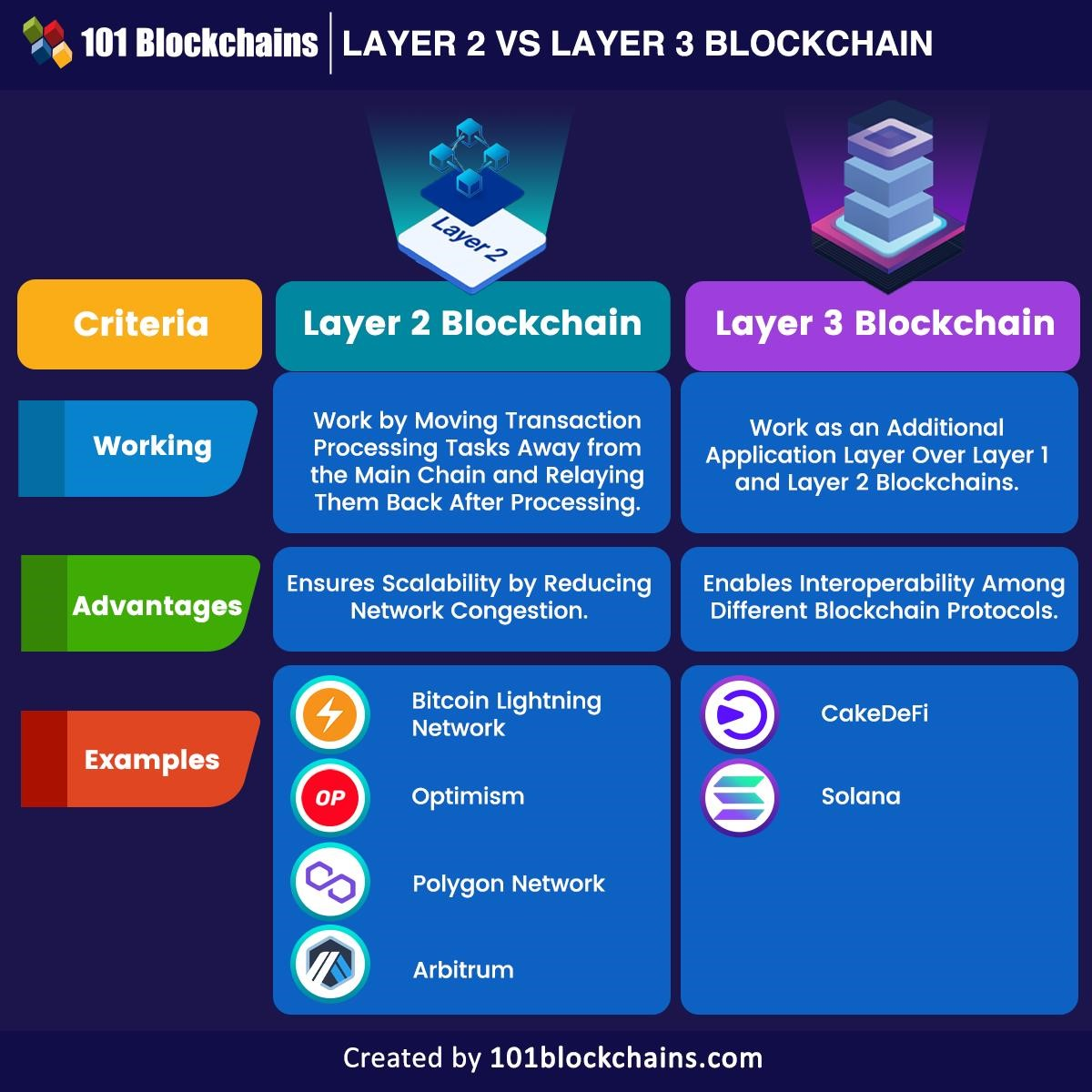
Bitcoin Lightning Network: This popular layer 2 solution built on the Bitcoin blockchain enables high-frequency transactions with minimal fees, faster settlement times, and reduced counterparty risks.
-
Optimism: Optimism utilizes optimistic rollups, bundling transactions in batches and sending them to the main Ethereum chain for validation, offering faster confirmation times and lower fees.
-
Polygon Network: Polygon is a widely adopted layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum. It leverages plasma implementations for efficient scalability and boasts a thriving dApp ecosystem.
-
Arbitrum: Developed by Off-chain Labs, Arbitrum offers a robust scaling solution for Ethereum, streamlining smart contract development and providing enterprise-grade scalability.
Layer 3 Networks: Enabling Interoperability
While layer 2 solutions enhance scalability, they don’t address the need for interoperability between different protocols. Layer 3 networks, a new application layer built upon layer 1 and layer 2 networks, fill this gap.
Layer 3 networks serve as a bridge between blockchain protocols, enabling seamless communication and data transfer between different chains. They facilitate interoperability between layer 1 and layer 2 networks, connecting various aspects of the blockchain and web3 landscape.
Comparing Layer 2 and Layer 3 Solutions
The key difference lies in their focus:
- Layer 2: Addresses scalability by offloading transactions and improving throughput.
- Layer 3: Enables interoperability between different blockchain networks and protocols.

The Bottom Line: A Collaborative Future
Layer 2 and layer 3 solutions are not competing; they are complementary forces driving the mainstream adoption of blockchain technology. Layer 2 focuses on improving user experience through scalability, resulting in lower costs and reduced network latency. Meanwhile, layer 3 networks unlock cross-chain functionality, enabling seamless communication between diverse protocols. Together, they pave the way for a more interconnected and accessible web3 ecosystem.

Learn more about us at: javanet247
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice. Always conduct your own research before making any investment decisions. 101 Blockchains is not responsible for any losses incurred based on the information provided in this article.